Helping Innovators Innovate.
Learn more about the Latest Diagnostic Research and Use Cases
The first clinically available seed-amplification assay that detects misfolded α-synuclein in cerebrospinal fluid—providing definitive biological evidence during a patient's lifetime.
Comprehensive guide to long-term biological sample storage. Learn best practices for tissue, blood, cell, and DNA/RNA preservation at optimal temperatures.
Learn how automated biobanking systems, robotic freezers, and AI-driven workflows are redefining biospecimen management and modern biostorage solutions.
Learn how to prevent freeze-thaw damage in biobanking and biorepository operations. Explore NCI and ISBER evidence-based best practices for biospecimen handling, freezer validation, and biostorage monitoring to protect sample integrity and regulatory compliance.
Fluorescence ultracentrifugation reveals how antibodies interact in serum, and Golden West’s Human Gamma Globulin Powder offers a reliable tool to replicate these conditions.
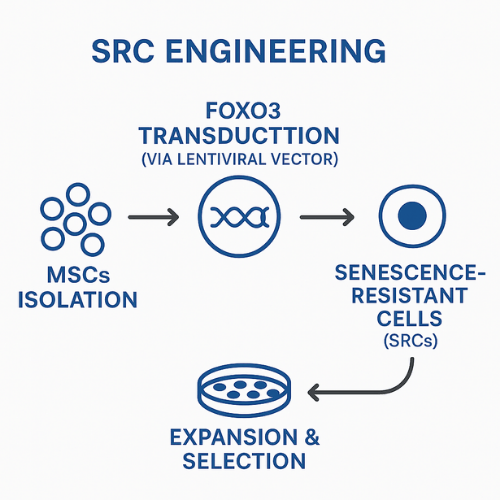
Discover how senescence-resistant human mesenchymal progenitor cells (SRCs), engineered to overexpress the longevity factor FOXO3, safely reversed aging markers across multiple tissues in aged macaques—offering a groundbreaking, multi‐system rejuvenation strategy for primates.
This study used APEX2 proximity labeling and high-purity luteinizing hormone to map the dynamic interactome of the LHR receptor—shedding light on GPCR signaling, trafficking, and key regulatory proteins RAP2B and RAB38 with nanometer precision.
Discover how a custom CRISPR base-editing therapy saved an infant with a rare genetic disorder—and why affordable, accessible genetic testing is now more critical than ever.
A big data study redefines 24-h urine cortisol reference ranges using LC-MS/MS—powered by MSG5000 matrix to ensure clean, accurate hormone quantification.
In the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), particularly for patients who cannot undergo intensive chemotherapy, emerging evidence is reshaping traditional expectations.
Vitamin A metabolism has long been seen as a job for the body’s own enzymes, primarily occurring in the liver and epithelial cells. But this study flips the script.
The primary aim of the study was to evaluate the efficacy of H4CBD on glucose intolerance and insulin resistance in OLETF rats, an established animal model for human metabolic syndrome —highlighting the utility of the MSG3200 human serum product along the way.
The importance of charcoal-stripped human serum in the study is particularly in the preparation of calibration standards and quality control samples for estrogen metabolite assays. The primary purpose of charcoal stripping is to eliminate endogenous hormones from the serum sample, creating a hormone-depleted medium for subsequent analyses.
Mass Spect Gold Human Serum Ultra-Low Vitamin D (MSG1000) product played a crucial role in the researchers' objective of developing a sensitive and cost-effective method for quantifying 1,25(OH)2D3 in human plasma. Here's how the MSG1000 was used to achieve their goal:
The MSG4000 product, a vitamin D–depleted human serum matrix, played a crucial role in the study. It served as a matrix for testing the antibody's extraction efficiency (analytical recovery) for different vitamin D metabolites. By adding each metabolite to MSG4000, extracting it with the immunoaffinity reagent, and then quantifying it with LC-MS/MS, the researchers determined how well the antibody captured each metabolite.
Hormone-free human serum serves as a baseline, enabling researchers to isolate the specific effects of their experimental variables with greater precision. By eliminating the confounding influences of hormones, scientists can investigate cellular responses, evaluate drug efficacy, and gain valuable insights into various biological pathways.
Utilizing Vitamin D free human serum improves the performance of diagnostic assays. It enhances the accuracy and sensitivity of the tests by reducing interference and minimizing false-positive/negative results caused by endogenous Vitamin D present in conventional serum samples. This leads to improved assay precision, reproducibility, and more reliable clinical interpretations.
TSH testing is a common diagnostic tool used in the evaluation of thyroid function. Traditional TSH testing measures the amount of TSH in the blood, but more recently, TSH free human serum has become a valuable tool in clinical diagnostics.
A series of studies have shown that when plants are under stress, they emit ultrasonic vibrations that can be heard by some animals, opening up a new avenue of research into the communication between plants and animals.
Recently, a significant breakthrough was made in superconductivity research. It has been shown that superconductivity can occur at near-ambient temperatures in a N-doped lutetium hydride. This discovery has the potential to revolutionize various fields, including transportation, energy, and computing.
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a specialized barrier that protects the central nervous system (CNS) from circulating molecules and pathogens. However, this barrier also limits the delivery of drugs and other therapeutic agents to the brain, which presents a significant challenge in the treatment of CNS diseases, including brain tumors. Albumin, a protein found in blood plasma, has been shown to have a key role in the delivery of anticancer compounds past the BBB.
Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique that can be used to identify the chemical composition of historical artifacts. The technique works by ionizing a sample and then measuring the mass-to-charge ratio of the resulting ions. Each element has a unique atomic mass, and when a sample is ionized, the ions produced will have a mass-to-charge ratio that is specific to the elements present in the sample.
MLMS is a soft ionization technique that involves depositing a matrix onto a sample before ionization. The matrix acts as a mediator to transfer energy to the sample, which results in the generation of ions. The resulting ions are then analyzed using MS. MLMS is a type of Desorption Electrospray Ionization (DESI) technique, which allows for the direct analysis of complex samples without the need for extensive sample preparation
IMS has several advantages over other analytical techniques. IMS is a fast technique, allowing for the analysis of large numbers of samples in a short amount of time. IMS is also highly sensitive, allowing for the detection of small amounts of analytes. IMS is also highly specific, allowing for the identification of different types of molecules based on their size, shape, and charge. In this blog post, we will discuss the applications of IMS in environmental health and food research and future trends in the field.